Where the barcode gets stuck
In an increasingly digitalised world, the link between physical objects and the associated data is becoming more and more important. The link in between, for automated data transfer, is usually formed by data carriers (barcodes, 2D codes or RFID tags). These data carriers must function. How well and whether they work, whether they can be read, can be checked by GS1 Austria. The evaluation of these checks always reveals deficiencies, as the result from 2018 also shows. Last year, 592 codes were checked and a qualified test report was sent.
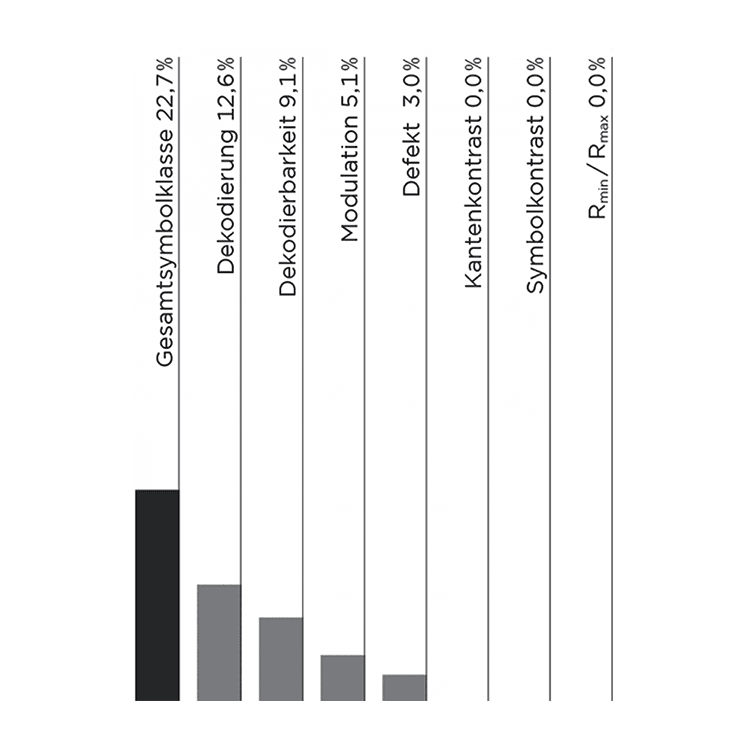
All errors that do not meet the minimum quality requirements (quality class 1.5) of GS1 are listed here. If a higher quality than 1.5 was required and not achieved, these errors were not included in the evaluation. Only the ISO parameters with more than 5 % errors were listed.
Total symbol class 22.7 % of the 198 symbols checked in 2018 according to ISO were incorrect.
Decoding (12.6 %): Determination of the information encoded in a barcode symbol. This can only be 4 (= good) or 0 (= bad). Poor decoding: wrong check digit, wrong code content, light zone too small, element or edge determination errors.
Decodability (9.1 %): The value indicates how well a barcode - depending on bars and spaces - is readable by a scanner.
Modulation (5.1 %): Uniformity of reflection ratios over the entire code; is the ratio of minimum edge contrast to symbol contrast.
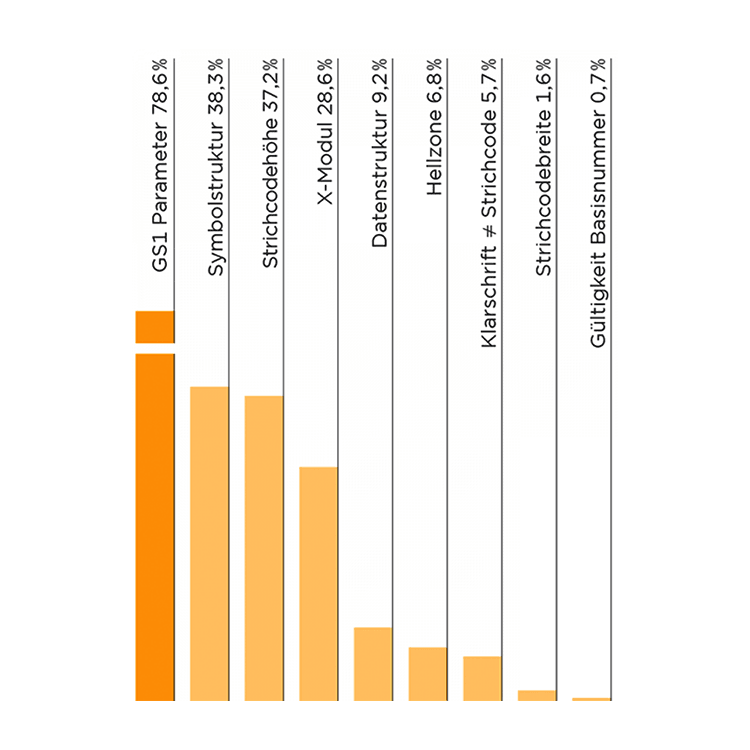
78 % of the codes checked were not GS1 compliant. Only the GS1 parameters with more than 5 % errors were listed.
Height (37.2 %): Height of the bars of a barcode.
X-module (28.6 %): X-module is the width of the narrowest element (bar, gap) of a barcode symbol.
Symbol structure (38.3 %): Basic technical error in a symbol, such as missing FNC1 character, incorrect check character or check digit or brackets encoded with the application identifier.
Data structure (9.2 %): Structure of the data in a barcode; error in the application of the data elements (application identifier).
Plain text line (5.7 %): Characters and letters below or near the symbol. The plain text line is a one-to-one representation of the encoded (user) data.
Bright zone (6.8 %): The zone before the start and after the stop sign of a barcode, which must be free of any interfering markings.
Exam starting at 15 euros
The fee for an audit according to ISO/IEC 15416/15415 and GS1 specifications of barcodes, 2D codes and GS1 transport labels is 40 euros. For GS1 Austria participants, two checks per month are free, further checks cost only 15 euros each.
Your contact person
Gerald Gruber
Project Manager GS1 System, Barcode Testing
gruber [at] gs1.at (gruber[at]gs1[dot]at)
A guest article by our partner GS1 Austria, design Starmühler
